NEO-E0: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ChipInfo | |||
|picture=aes_e0.jpg | |||
|pkg=QFP64R | |||
|manu=fujitsu | |||
|date=1991 ? | |||
|gates= | |||
|used_on={{PCB|NEO-AES3-3}} ... | |||
}} | |||
Just a 24-bit buffer and logic for [[68k vector table]] swapping. | |||
= | =68k vector table swapping= | ||
The 68k vector table seen by the 68k is selected by writing to {{Reg|REG_SWPROM}} (table from the game) or {{Reg|REG_SWPBIOS}} (table from the [[system ROM]]). | |||
A22Z and A23Z are used in place of A22 and A23 to make the address appear to address decoding chips as a system ROM access instead of a [[P ROM]] access. | |||
The {{Sig|VEC|VEC}} signal comes from the 74H259 system latch. | |||
{|class="wikitable" | |||
!rowspan=2|Address||colspan=2|Maps to | |||
|- | |||
!VEC = 0||VEC = 1 | |||
|- | |||
|$000000~$00007F||$C00000~$C0007F||$000000~$00007F | |||
|- | |||
|$000080~$BFFFFF||colspan=2|No change | |||
|- | |||
|$C00000~$C0007F||$000000~$00007F||$C00000~$C0007F | |||
|- | |||
|$C00080~$FFFFFF||colspan=2|No change | |||
|} | |||
= | Verilog from [[User:Kyuusaku]]: | ||
<pre>{A23Z,A22Z} = A[23:22] ^ 2{~|{A[21:7],^A[23:22],VEC}}</pre> | |||
[[File:Neo-e0_pinout.png]] | =Pinouts= | ||
==Input to output map== | |||
* 64 -> 5 | |||
* 1 -> 6 | |||
* 2 -> 7 | |||
* 3 -> 8 | |||
* 4 -> 9 | |||
* 15 -> 11 | |||
* 16 -> 12 | |||
* 17 -> 13 | |||
* 18 -> 14 | |||
* 19 -> 22 | |||
* 20 -> 23 | |||
* 21 -> 24 | |||
* 31 -> 27 | |||
* 32 -> 28 | |||
* 33 -> 29 | |||
* 34 -> 30 | |||
* 36 -> 39 | |||
* 37 -> 40 | |||
* 38 -> 41 | |||
* 48 -> 43 | |||
* 49 -> 44 | |||
* 50 -> 45 | |||
* 51 -> 46 | |||
* 52 -> 47 | |||
* 53 -> 55 if VEC is high | |||
* 54 -> 56 if VEC is high | |||
==Console== | |||
On the AES, the AND gate is used to make /SROMOE from (/SROMOEL AND /SROMOEU). | |||
==MV2B & MV2-01 @ H7 pinout== | |||
* 55 = sPCK1B | |||
* 56 = sPCK2B | |||
[[P_bus]] buffer | |||
==MV2B @ G2 pinout== | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
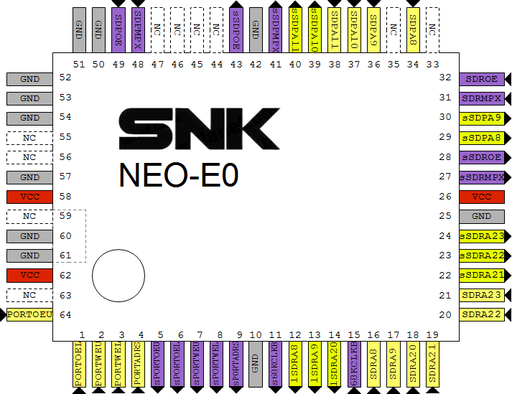
[[File:Neo-e0_G2_pinout.png|512px]] | |||
OpenOffice Draw file: [[File:Neo-e0_mv2b_G2.odg]] | |||
| | |||
*A1~A23: [[68k]] address bus | |||
*MCA0~MCA23: [[memory card]] address bus | |||
*BNK0~BNK2: memory card banking from [[NEO-D0]] | |||
*VEC: [[System ROM]] vector table swapping enable | |||
|} | |||
==MV2B @ F7 pinout== | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
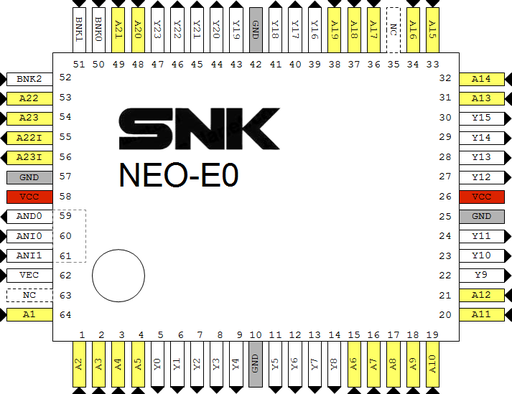
[[File:Neo-e0_F7_pinout.png|512px]] | |||
OpenOffice Draw file: [[File:Neo-e0_mv2b_F7.odg]] | |||
| | |||
Acts just as a buffer. | |||
*s*: signals to both slots | |||
|} | |||
==MV2F @ E1 pinout (to be confirmed) and AES== | |||
{| | |||
| | |||
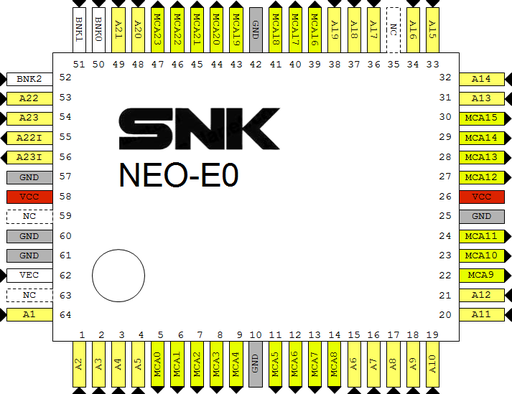
[[File:Neo-e0_pinout.png|512px]] | |||
OpenOffice Draw file: [[File:neo-e0.odg]] | OpenOffice Draw file: [[File:neo-e0.odg]] | ||
| | |||
*A1~A23: 68k address bus | *A1~A23: 68k address bus | ||
*Y0~Y23: memory card address bus | *Y0~Y23: memory card address bus | ||
*BNK0~BNK2: comes from [[NEO-D0]], | *BNK0~BNK2: comes from [[NEO-D0]], [[memory card]] bank | ||
*VEC: | *VEC: System ROM vector table swapping | ||
*ANI0, ANI1, AND0: AND gate used to generate ROMOE from ROMOEU and ROMOEL | *ANI0, ANI1, AND0: AND gate used to generate ROMOE from (ROMOEU and ROMOEL) | ||
|} | |||
[[Category:Chips]] | [[Category:Chips]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:19, 18 July 2022

| |
| Package | QFP64R |
| Manufacturer | |
| First use | 1991 ? |
| Used on | NEO-AES3-3 ... |
Just a 24-bit buffer and logic for 68k vector table swapping.
68k vector table swapping
The 68k vector table seen by the 68k is selected by writing to REG_SWPROM (table from the game) or REG_SWPBIOS (table from the system ROM).
A22Z and A23Z are used in place of A22 and A23 to make the address appear to address decoding chips as a system ROM access instead of a P ROM access.
The VEC signal comes from the 74H259 system latch.
| Address | Maps to | |
|---|---|---|
| VEC = 0 | VEC = 1 | |
| $000000~$00007F | $C00000~$C0007F | $000000~$00007F |
| $000080~$BFFFFF | No change | |
| $C00000~$C0007F | $000000~$00007F | $C00000~$C0007F |
| $C00080~$FFFFFF | No change | |
Verilog from User:Kyuusaku:
{A23Z,A22Z} = A[23:22] ^ 2{~|{A[21:7],^A[23:22],VEC}}
Pinouts
Input to output map
- 64 -> 5
- 1 -> 6
- 2 -> 7
- 3 -> 8
- 4 -> 9
- 15 -> 11
- 16 -> 12
- 17 -> 13
- 18 -> 14
- 19 -> 22
- 20 -> 23
- 21 -> 24
- 31 -> 27
- 32 -> 28
- 33 -> 29
- 34 -> 30
- 36 -> 39
- 37 -> 40
- 38 -> 41
- 48 -> 43
- 49 -> 44
- 50 -> 45
- 51 -> 46
- 52 -> 47
- 53 -> 55 if VEC is high
- 54 -> 56 if VEC is high
Console
On the AES, the AND gate is used to make /SROMOE from (/SROMOEL AND /SROMOEU).
MV2B & MV2-01 @ H7 pinout
- 55 = sPCK1B
- 56 = sPCK2B
P_bus buffer
MV2B @ G2 pinout
|
OpenOffice Draw file: File:Neo-e0 mv2b G2.odg |
|
MV2B @ F7 pinout
|
OpenOffice Draw file: File:Neo-e0 mv2b F7.odg |
Acts just as a buffer.
|
MV2F @ E1 pinout (to be confirmed) and AES
|
OpenOffice Draw file: File:Neo-e0.odg |
|