VRAM: Difference between revisions
m (minor edits) |
m (Minor details, some rephrasing) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* {{Reg|REG_VRAMMOD ($3C0004)}} is the signed value added to the VRAM address after a write | * {{Reg|REG_VRAMMOD ($3C0004)}} is the signed value added to the VRAM address after a write | ||
The original SNK documentation specifies that the address register should be set directly instead of | The original [[Official development manual|SNK documentation]] specifies that the address register should be set directly instead of counting on incrementation when crossing VRAM zones ($0000~$7FFF to/from $8000~$FFFF) i.e. when bit 15 has to change. This is a side effect of simplifications in the [[GPU]]. | ||
== Memory map == | == Memory map == | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|$7500 | |$7500 | ||
|$7FFF | |$7FFF | ||
|[[Fix bankswitching| | |[[Fix bankswitching|Fix map extension]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|$8000 | |$8000 | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
|} | |} | ||
Even if VRAM can be | Even if VRAM can be accessed at any time (even during active display), it is not dual-ported so some timing restrictions have to be met in order to avoid skipping writes or reading data too early after setting the address. This is because LSPC has to interleave VRAM access between the rendering process and the CPU. | ||
== Timing considerations == | == Timing considerations == | ||
The following timings are given to be 100% sure that no read or write to VRAM will fail. It | The following timings are given to be 100% sure that no read or write to VRAM will fail. It might be possible to sometimes shorten them with extreme guessing methods on the CPU's side, but it's practically useless. | ||
After a write: | After a write: | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
After an address change, reads should be made after at least 16 CPU cycles. | After an address change, reads should be made after at least 16 CPU cycles. | ||
Note that these | Note that these restrictions only concern VRAM access, and not the internal LSPC registers. | ||
[[Category:Video system]] | [[Category:Video system]] | ||
Revision as of 02:36, 31 March 2016
VRAM stands for Video RAM.
The NeoGeo has 68KiB (physically 64KiB + 4KiB, respectively called lower and upper, or slow and fast) of VRAM accessible as 16 bits words, which is used to store sprite attributes, the fix layer tile map and sprite lists for video rendering. Contrary to other systems, the VRAM here does not contain actual graphics.
Access to VRAM is done through 3 Memory mapped registers handled by the GPU, it isn't mapped in the 68k address space. Every VRAM address points to a word, not a byte.
- REG_VRAMADDR ($3C0000) sets the VRAM address for the next read/write operation
- REG_VRAMRW ($3C0002) is the data read or to write
- REG_VRAMMOD ($3C0004) is the signed value added to the VRAM address after a write
The original SNK documentation specifies that the address register should be set directly instead of counting on incrementation when crossing VRAM zones ($0000~$7FFF to/from $8000~$FFFF) i.e. when bit 15 has to change. This is a side effect of simplifications in the GPU.
Memory map
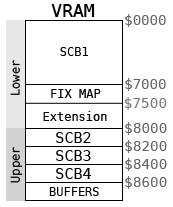
| Start | End | Description |
| $0000 | $6FFF | SCB1 |
| $7000 | $74FF | Fix map |
| $7500 | $7FFF | Fix map extension |
| $8000 | $81FF | SCB2 |
| $8200 | $83FF | SCB3 |
| $8400 | $85FF | SCB4 |
| $8600 | $867F | Sprite list for even scanlines |
| $8680 | $86FF | Sprite list for odd scanlines |
Even if VRAM can be accessed at any time (even during active display), it is not dual-ported so some timing restrictions have to be met in order to avoid skipping writes or reading data too early after setting the address. This is because LSPC has to interleave VRAM access between the rendering process and the CPU.
Timing considerations
The following timings are given to be 100% sure that no read or write to VRAM will fail. It might be possible to sometimes shorten them with extreme guessing methods on the CPU's side, but it's practically useless.
After a write:
- Another write should be made after at least 12 cycles.
- An address change should be made after at least 16 cycles.
After an address change, reads should be made after at least 16 CPU cycles.
Note that these restrictions only concern VRAM access, and not the internal LSPC registers.